👉 Note: All Docker notes
What and Why?
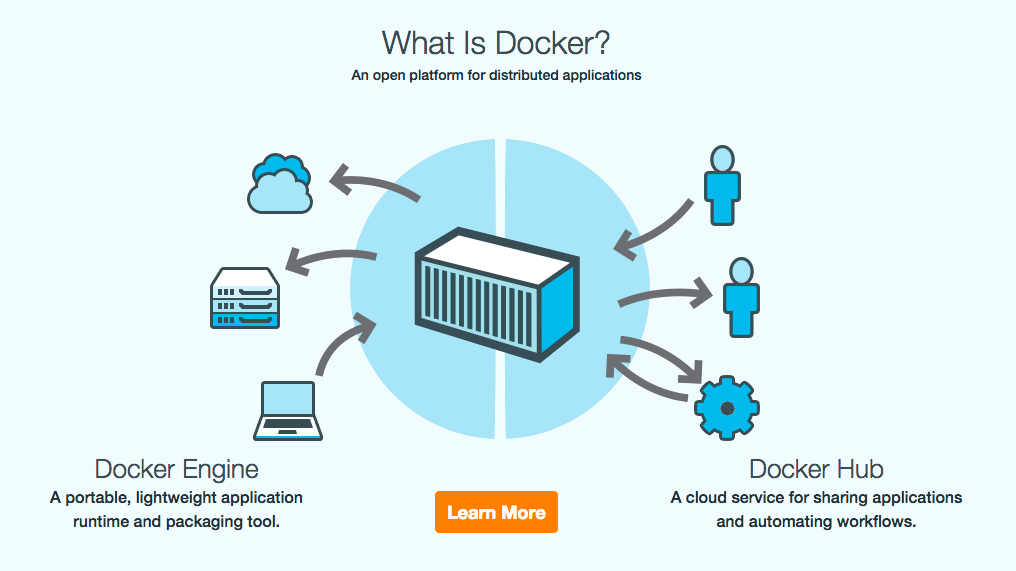
Souce rollout.io.
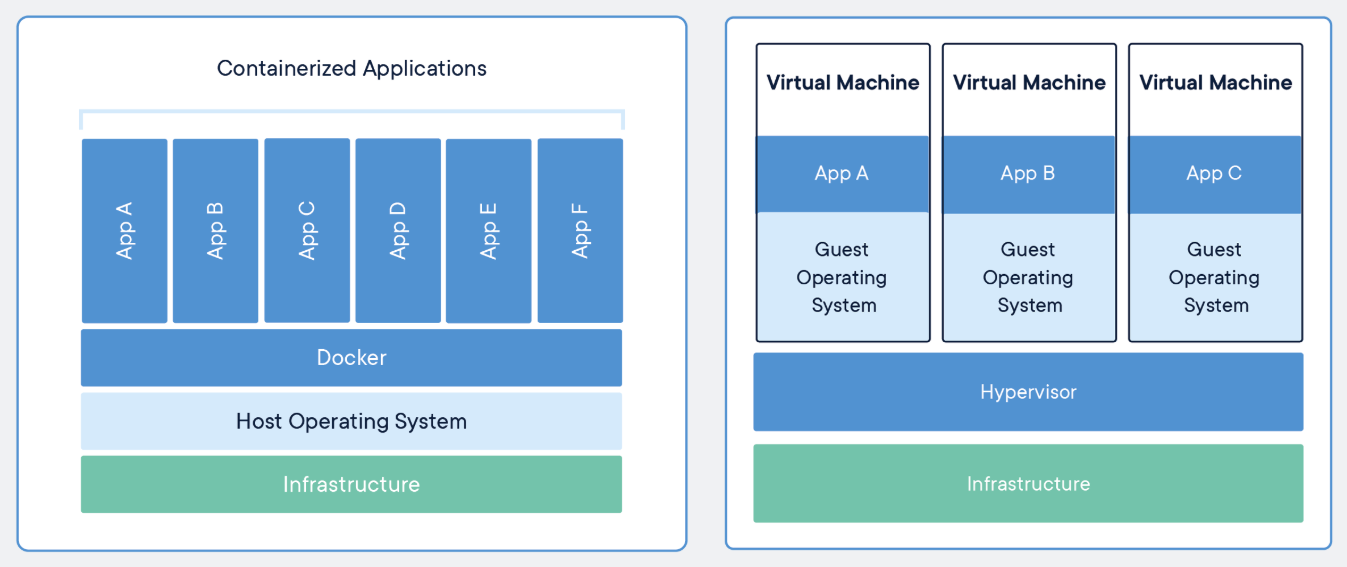
Container vs Virtual Machine, souce docker.com.
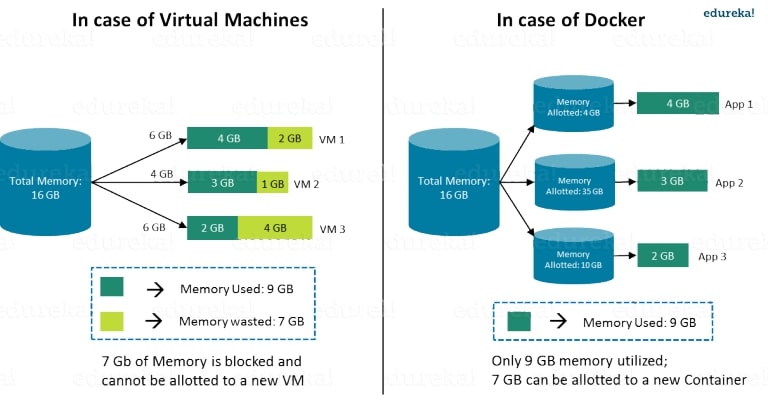
RAM usage: Docker vs Virtual Machine, souce eureka.com.
Abbreviate
ps= process status : check running containers (with-afor all)-i= interactive : used indocker execordocker run-t= terminal : used indocker execordocker run-m= memory-vor--volume: corresponding folders in/out containers.--rm: create temprarily a container (removed after exit)
Installation
👉 For all platforms, check official guide. It's up to date!
- You mind find this article is useful for Ubuntu/Pop!_OS.
- After installing, if you meet
Got permission denied while trying to connect to the Docker daemon socket, check this.
For Linux, check this!
Show codesUnninstall old versions
sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io containerd runc
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install \
apt-transport-https \
ca-certificates \
curl \
gnupg-agent \
software-properties-common
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -Make sure:
9DC8 5822 9FC7 DD38 854A E2D8 8D81 803C 0EBF CD88sudo apt-key fingerprint 0EBFCD88
sudo add-apt-repository \
"deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs) \
stable"Install docker engine
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.ioCheck if everything is ok
sudo docker run hello-worldIncase docker-compose isn't installed
sudo apt install docker-composeIf you use Ubuntu 20.04+, replace
$(lsb_release -cs)witheoanbecause docker currently (17 May 20) doesn't support 20.04 yet!If wanna run docker without
root, check this.sudo groupadd docker # create a docker group
sudo usermod -aG docker <user> # add <user> to group
newgrp docker # activate the changesConfigure docker start on boot (Ubuntu 15.04 or later)
sudo systemctl enable docker
👉 Check this.
👉 Note: Docker + WSL2
You must have Windows 10: Pro, Enterprise, or Education (Build 15063 or later). Check other requirements.
# POWERSHELL
# check window version
Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_OperatingSystem | % Caption
# check window build number
Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_OperatingSystem | % BuildnumberActive Hyper-V and Containers (you can do it manually in Turn Windows features on or off)
# Open PowerShell with Administrator and run following
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName containers –All
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V –All
# restart- Download and install.
- Check
docker version. - Try
docker run hello-world.
Check this note.
Uninstall
Linux
# from docker official
sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io containerd runc# identify what installed package you have
dpkg -l | grep -i docker
# uninstall
sudo apt-get purge -y docker-engine docker docker.io docker-ce docker-ce-cli
sudo apt-get autoremove -y --purge docker-engine docker docker.io docker-ce# remove images containers
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker /etc/docker
sudo rm /etc/apparmor.d/docker
sudo groupdel docker
sudo rm -rf /var/run/docker.sockLogin & Download images
docker login
# using username (not email) and password- Download at Docker Hub.
- Download images are store at
C:\ProgramData\DockerDesktop\vm-data(Windows) by default.
Check info
# docker's version
docker --versionImages
# list images on the host
docker images# check image's info
docker inspec <image_id># Where are images stored?
docker info
# normally, /var/lib/docker/Containers
# list running containers
docker ps
docker ps -a # all (including stopped)# only the ids
docker ps -q
docker ps -a -q# container's size
docker ps -s
docker ps -a -s# container's names only
docker ps --format '{{.Names}}'
docker ps -a --format '{{.Names}}'# Check the last command in container
docker ps --format '{{.Command}}' --no-trunc# check log
# useful if we wanna see the last running tasks's
docker container logs <container_name># get ip address
docker inspect <container_name> | grep IPAddress# Attach to the running container
docker attach <container_name>Others
# RAM & CPU usages
docker stats
docker stats <container_name>Attach / Start / Stop
We can use sometimes interchangeable between <container_id> and <container_name>.
# get info (container's id, image's id first)
docker ps -a# start a stopped container
docker start <container_id>
# start and enter the container
docker start -i <container># stop a container
docker stop <container_id># Entering the running container (not attach)
docker exec -it <container_name> bash# stop all running containers
docker stop $(docker ps -a -q)# Attach to the running container
docker attach <container_name>Delete
Read more here.
Everything
# any resources
docker system prune# with all unused images
docker system prune -aImages
# list all images
docker images -a# remove a specific image
docker image rm <IMAGE_ID>Dangling images are layers that have no relationship to any tagged images.
# list dangling images
docker images -f dangling=true# remove dangling images
docker images purgeIf you use docker images -a and see a lot of <none>:<none> images. Don't be worry to fast, if they're dangling images, they take spaces, otherwise, they're harmless to your drive! Check this SO.
Containers
# remove a specific containers
docker rm -f <container-id># remove all containers
docker rm -f $(docker ps -a -q)Zsh in a container
If you have already a container, enter that container and then,
# Enter
docker exec -it container_name bash
# Install zsh
apt-get update
apt-get install zsh
zsh
# Install curl
apt-get install curl
# Install oh-my-zsh
sh -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/robbyrussell/oh-my-zsh/master/tools/install.sh)"If you want to integrate the zsh installation in the Dockerfile,
RUN apt-get install zsh && apt-get install curl
RUN PATH="$PATH:/usr/bin/zsh"
RUN sh -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/robbyrussell/oh-my-zsh/master/tools/install.sh)"Now, enter the container by docker exec -it zsh (instead of bash)!
Build an image
Create
# build image with Dockerfile
docker build -t <img_name> .
# custom Dockerfile.abc
docker build -t <img_name> . -f Dockerfile.abc# with docker-compose
docker-compose up
# with custom file
docker-compose -f docker-compose.amin.yml up -d# if success
# service name "docker_thi"
docker run -it <service_name> bash# from current container
docker ps -a # check all containers
docker commit <container_id> <new_image_name>Rename
docker image tag old:latest myname/new:latestDockerfile
👉 Official doc: Best practices for writing Dockerfiles
FROM nvidia/cuda:10.2-base
# encoding
ENV LANG en_US.UTF-8
ENV LANGUAGE en_US:en
ENV LC_ALL en_US.UTF-8
# fix (tzdatachoose)
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
RUN apt-get -y update && \
apt-get -y upgrade && \
apt-get install -y openssh-server && \
apt-get install -y python3-pip python3-dev locales git r-base
# ssh server
RUN mkdir /var/run/sshd
RUN echo 'root:qwerty' | chpasswd
RUN sed -i 's/#PermitRootLogin prohibit-password/PermitRootLogin yes/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# SSH login fix. Otherwise user is kicked off after login
RUN sed 's@session\s*required\s*pam_loginuid.so@session optional pam_loginuid.so@g' -i /etc/pam.d/sshd
# need?
ENV NOTVISIBLE "in users profile"
RUN echo "export VISIBLE=now" >> /etc/profile
# create alias
RUN echo 'alias python="python3"' >> ~/.bashrc
RUN echo 'alias pip="pip3"' >> ~/.bashrc
# create shortcuts
RUN ln -s /abc/xyz /xyz/xyz
# install python's requirements
COPY requirements_dc.txt requirements.txt
RUN python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip && \
python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt
COPY . .
# export port ssh
EXPOSE 22
COPY script.sh starting_script.sh
# run
CMD ["sh","-c","cd /data_controller/utils/ && sh generate_grpc_code_from_protos.sh && cd /srv/ && sh starting_script.sh"]FROM ubuntu:20.04
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y openssh-server
RUN mkdir /var/run/sshd
RUN echo 'root:THEPASSWORDYOUCREATED' | chpasswd
RUN sed -i 's/#*PermitRootLogin prohibit-password/PermitRootLogin yes/g' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# SSH login fix. Otherwise user is kicked off after login
RUN sed -i 's@session\s*required\s*pam_loginuid.so@session optional pam_loginuid.so@g' /etc/pam.d/sshd
ENV NOTVISIBLE "in users profile"
RUN echo "export VISIBLE=now" >> /etc/profile
EXPOSE 22
CMD ["/usr/sbin/sshd", "-D"]For more about ssh connection, check official doc.
If .env doesn't work? => This is expected. SSH wipes out the environment as part of the login process. [ref]
# For example, all environement variables are stored in a
# /home/thi/.env
# add them to container's env
cat /home/thi/.env >> /etc/environment
# exit current ssh session
# connect again
# check
envFROM: the base image you use, can be obtained from Docker Hub. For example,FROM ubuntu:18.04(18.04is a tag,latestis default)WORKDIR app/: Useapp/as the working directory.RUN: install your application and packages requited, e.g.RUN apt-get -y update.RUN <command>(shell form)RUN ["executable", "param1", "param2"](exec form)
CMD: sets default command and/or parameters, which can be overwritten if docker container runs with command lines. If there are manyCMDs, the last will be used.# in Dockerfile
CMD echo "Hello world"
# run only
docker run -it <image>
# output: "Hello world"
# run with a command line
docker run -it <image> /bin/bash
# output (CMD ignored, bash run instead): root@7de4bed89922:/#CMD ["executable","param1","param2"](exec form, preferred)CMD ["param1","param2"](sets additional default parameters forENTRYPOINTin exec form)CMD command param1 param2(shell form)- Multiple commands:
CMD ["sh","-c","mkdir abc && cd abc && touch new.file"]
ENTRYPOINT: configures a container that will run as an executable. Look likeCMDbutENTRYPOINTcommands and parameters are not ignored when Docker container runs with command line parameters.More detail# Dockerfile
ENTRYPOINT ["/bin/echo", "Hello"]
CMD ["world"]
# run
docker run -it <image>
# produces 'Hello world'
# but run
docker run -it <image> John
# produces 'Hello John' (only CMD command is override)ENTRYPOINT ["executable", "param1", "param2"](exec form, preferred)ENTRYPOINT command param1 param2(shell form)
Check this SO for
CMDvsENTRYPOINT.EXPOSE 5000: Listen on the specified portCOPY . app/: Copy the files from the current directory toapp/
You cannot use something like COPY .. . (parent of the folder containing the Dockerfile) in the Dockerfile because it uses the "build context" and it can access to files within that context. Ref.
In the Dockerfile, change COPY .. . to COPY . ..
Next, cd .. (go to the parent of the folder containing the Dockerfile, let's say docker/) and then use option -f docker/Dockerfile when you build an image.
Or you can use something below (no need to cd ..)
docker build -f ../DockerfileIf we run multiple interative commands (wait for action), for example, a jupyter notebook with a ssh server, we cannot put them directly in CMD command.
Solution: using a file .sh and put & at the end of the 1st command like:
$(which sshd) -Ddp 22 &
jupyter lab --no-browser --allow-root --ip=0.0.0.0 --NotebookApp.token='' --NotebookApp.password=''Create a container
CLI
# container test from an image
docker create --name container_test -t -i <image_id> bash
docker start container_test
docker exec -it container_test bashdocker run --name <container_name> -dp 3000:3000 -v todo-db:/etc/todos <docker_img># run a command in a running docker without entering to that container
# e.g. running "/usr/sbin/sshd -Ddp 22"
docker exec -it -d docker_thi_dc /usr/sbin/sshd -Ddp 22
# "-d" = Detached mode# want docker auto removes a container after exit
docker run --rm ...docker-compose.yml
Use to create various services with the same image.
docker-compose up -d # up and detach
docker-compose -f file_name.yml up -d # custom docker-compose.yml file name
# if you run 2 container in the same folder name
docker-compose -p "project_1" up -d
docker-compose -p "project_2" up -d# docker-compose.yml
#------------------------------
# run by `docker-compose up`
version: '3'
services:
dataswati:
container_name: docker_thi
image: docker_thi_img:latest
ports:
- "8888:8888"
volumes:
- "/local-folder/:/docker-folder/"
working_dir: /srvTo upgrade docker-compose file format from version 2.x to version 3.x, check this guide. Also check this: Compose file versions and upgrading.
depends_on:[ref] Express dependency between services (with orders).In
docker-compose.yml:dbandredisstart beforeweb.version: "3.8"
services:
web:
build: .
depends_on:
- db
- redis
redis:
image: redis
db:
image: postgrescommand:[ref] Override the default command.stdin_open: trueandtty: true: keep container alive!volumes(outside containers): volumes controlled by docker. They're located on different places,# check info of a volume
docker volume inspect <volume_name>restart: always(auto start container after logging in),no(default),on-failure.build: <dir_to_Dockerfile_file>: build an image before usingdocker-compose.runtime: nvidia: ifdocker-compose --versionhigher than 2.3 and there is NVIDIA GPU on your computer (check more detail in this note).
🔅 If there is no already built image, you can use a Dockerfile in the same place as docker-compose.yml. In docker-compose.yml, use
services:
dataswati:
build: .Then run docker-compose up --build.
🔅 Update to the newer version of docker-compose? Included in Docker Desktop (on Windows and MacOS), read this SO (Linux).
Errors
Docker can't connect to docker daemon`.
# check if daemon is running?
ps aux | grep docker
# run
sudo /etc/init.d/docker startsudo systemctl restart docker meets Job for docker.service failed because the control process exited with error code.
- Try to remove failed
daemon.jsonfile in/etc/docker/(if the problem comes from here) - Try running either
sudo /etc/init.d/docker startorsudo service docker restart(twice if needed).
perl: warning: Please check that your locale settings: when using below in the Dockerfile,
ENV LANG en_US.UTF-8
ENV LANGUAGE en_US:en
ENV LC_ALL en_US.UTF-8
# Replace them by
RUN echo "LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8" >> /etc/environment
RUN echo "en_US.UTF-8 UTF-8" >> /etc/locale.gen
RUN echo "LANG=en_US.UTF-8" > /etc/locale.conf
RUN locale-gen en_US.UTF-8# On Windows + WSL2
The process cannot access the file 'ext4.vhdx' because it is being used by another process.- Quit docker.
- Open Task Manager, try to end the processes wsappx (all of them).
- Reopen docker.
Reference
- Play with Docker -- right on the web.
- Yury Pitsishin -- Docker RUN vs CMD vs ENTRYPOINT.
- What is the difference between devel and runtime tag for a Docker container? - Stack Overflow

💬 Comments