The last modifications of this post were around 4 years ago, some information may be outdated!
This is a draft, the content is not complete and of poor quality!
On this page
What & Why?
To check the similar distribution of 2 samples drawn from population. If these samples are normal, we can use T-test, but if they are not normal, we need to use KS-test. KS-test is a non-parametric test.
Null hypothesis (): "Two samples drawn from population with the same distribution."
👉 Read more about p-value. We use this value to evaluate the true/false of above null hypothesis.
The difference (in use) of T-test (need an assumption of nomality) and KS-test (don't need),
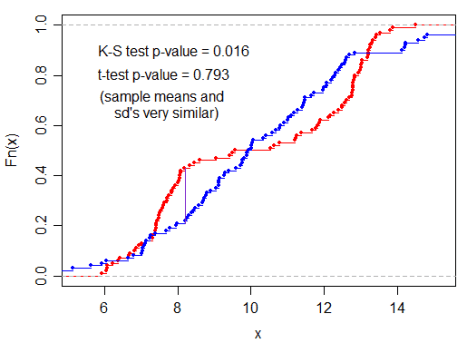
- Two samples have the same mean & standard deviation ⇒ p-value is high ⇒ cannot reject (not true)
- KS-test can detect the variance ⇒ p-value is low ⇒ we can reject ⇒ 2 samples are not the same distribution!!! (yep!)
How?
If the KS statistic is small or the p-value is high, then we cannot reject the hypothesis that the distributions of the two samples are the same.
Code?
from scipy import stats# one-sample KS test
stats.kstest(x, 'norm')# two-sample KS test
stats.ks_2samp(x, y)References
- Matthew E. Clapham -- 10: Kolmogorov-Smirnov test (video)
- An example of why we need to use EMD instead of Kolmogorov–Smirnov distance (video).

💬 Comments